


You may wear it for 24 to 48 hours and sometimes longer.
EXTRA HEARTBEAT NAME PORTABLE
Holter: A Holter is a portable ECG that your doctor will send you home with.The ECG takes just a couple of minutes to perform. There are certain ECG signatures that act as red flags for underlying structural cardiac disease. Your cardiac electrophysiologist is able to use the ECG to identify the exact PVC location in the heart. The ECG is useful in identifying the “extra beat” or PVC. This data is fed to a "computer" to generate an "electrical graph" on a piece of paper, otherwise known as the 12 lead electro cardiogram (ECG). Standard 12 lead ECG : This test is done in a clinical or hospital setting where electrical signals from the heart are gathered via 12 electrodes that are attached to the chest wall.PVCs may also indicate an underlying structural heart disease such as ischaemic heart disease or cardiomyopathies, including ARVC. Triggers for the PVCs include medications that have a stimulant effect on the heart, as well as caffeine, alcohol, illicit drugs and states of heightened sympathetic activity like stress or exercise. It is possible for individuals with structurally normal hearts of any age to experience PVCs. It may also be a marker for underlying cardiomyopathy, including ARVC. Sometimes PVCs may reflect an underlying abnormal heart substrate, especially when the PVCs don't come from the outflow tracts, and this tends to occur more commonly in elderly people and in individuals with underlying structural heart disease, including a history of a heart attack. These PVCs have a predilection for the outflow tract regions of the heart as this is close to where the major arteries exit the ventricles. Sometimes people with a structurally normal heart have a high burden of PVCs. The percentage of PVCs typically increases with age. They can vary from 0.5% to 3% of the normal heartbeats in 24-hour Holter recordings. PVCs occur in almost everyone at some stage. Symptoms of occasionalventricular contractionsmay not be serious at first, but chronicventricular contractionssuggest an underlying heart condition that requires treatment urgently. This may cause symptoms of weakness or fatigue in some individuals. In cases where the PVC burden is high, there is emerging evidence to demonstrate that this may lead to weakened ventricles, also known as ventricular dysfunction. If the PVCs are fast and sustained for long periods at a time (in the case of ventricular tachycardia, for example), the individual may experience what is known as “transient loss of consciousness”, a condition also referred to as syncope. This can lead to symptoms like dizziness or presyncope. Although it is quite unusual, PVCs can cause lowered blood pressure. If the PVCs are more sustained, this may give a sensation of a fast heartbeat or heart flutter. Single PVCs give the feeling of a “missed” or “skipped” heartbeat. What are the symptoms of PVCs?Īs the beat following the PVC is more vigorous than usual, some common symptoms may include chest heaviness, discomfort or pain.
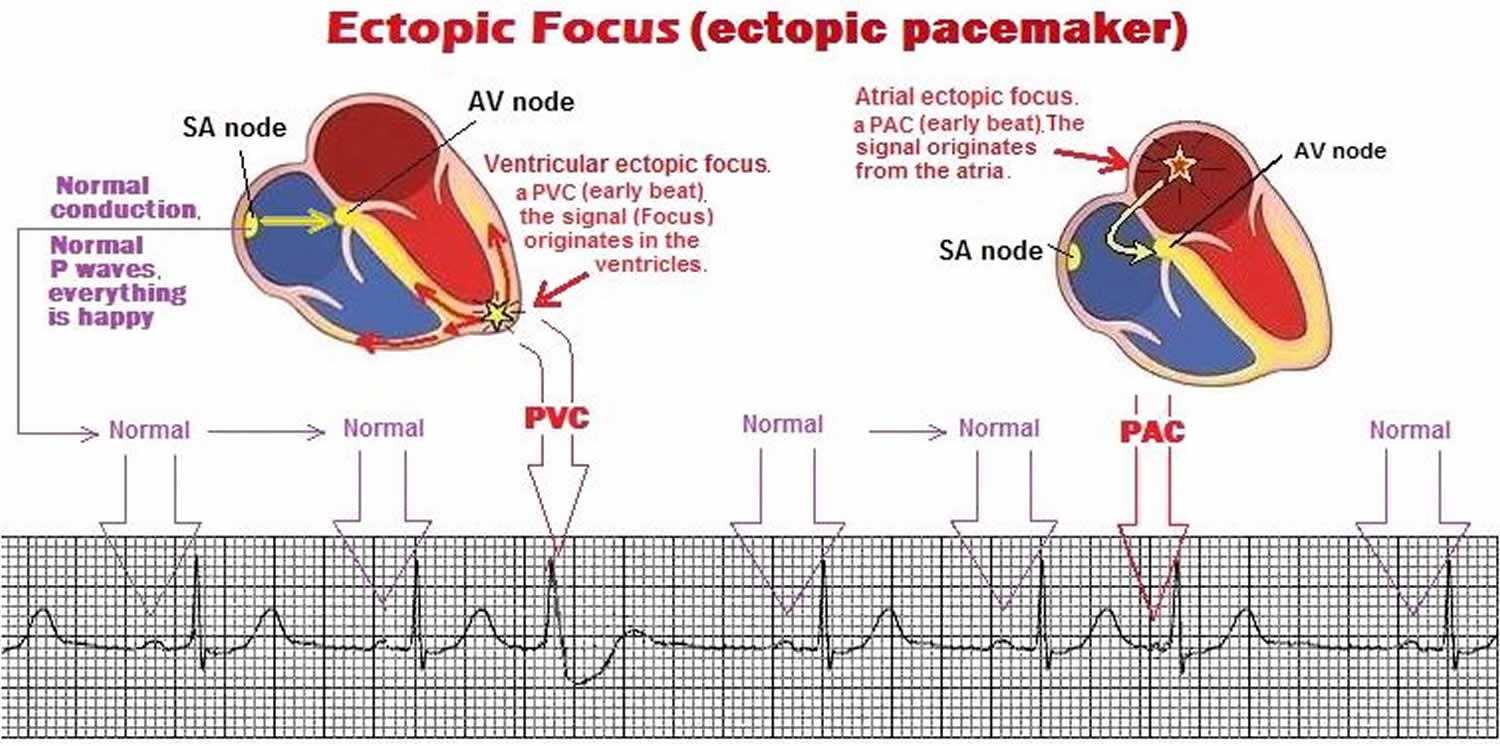
If more than three PVCs occur in a row, it can be identified as ventricular tachycardia. If it occurs after every second normal beat, it is called ventricular trigeminy, and if it occurs after every third beat, it is called ventricular quadrigeminy. A PVC that occurs after every normal beat is called ventricular bigeminy. Sometimes the PVCs can occur in a very regular, predictable manner. During the pause that occurs after the PVV, the ventricles are filled with more than the usual volume of blood, which results in the extra beat contracting more vigorously. This is followed by a slight pause and a beat that is more vigorous than usual. The arrhythmia is characterised by the following “abnormal rhythm”: A normal beat is followed by an extra beat from the ventricle (PVC). The extra heartbeat disrupts the regular heartbeat, affecting the heart rhythm. What are premature ventricular contractions?Ī premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is an extra heartbeat that arises from the lower half of the heart (otherwise known as the ventricle).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
